参数测试
Parameterized Runner实现了参数测试,当跑一个参数测试类的时候,它的实例是由测试方法和测试数据的元素交叉创建的
举例,如下Fibonacci方法:
package com.junit.learning.parameterized;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest {
@Parameterized.Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 1}, {3, 2}, {4, 3}, {5, 5}, {6, 8}
});
}
private int fInput;
private int fExpected;
public FibonacciTest(int input, int expected) {
fInput = input;
fExpected = expected;
}
@Test
public void test() {
assertThat(fExpected).isEqualTo(Fibonacci.compute(fInput));
}
}
FibonacciTest的每个参数都由两个参数的构造方法和标记了@Parameters注解的方法中的值来创建. FibonacciTest运行测试类时的执行顺序如下:
1. 首先会初始化@Parameters注解标记的数据.
2. 然后循环这些数据
3. 每一个循环中的值都会传递(注入)到构造函数FibonacciTest(int input, int expected)中
4. test()中的断言
使用@Parameter注入属性(不再用构造函数)
也可以使用@Parameter注解将值注入到字段中,而不需要构造方法.如下
package com.junit.learning.parameterized;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest2 {
@Parameterized.Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 1}, {3, 2}, {4, 3}, {5, 5}, {6, 8}
});
}
@Parameterized.Parameter // first data value (0) is default
public /* NOT private */ int fInput;
@Parameterized.Parameter(value = 1)
public /* NOT private */ int fExpected;
@Test
public void test() {
assertThat(fExpected).isEqualTo(Fibonacci.compute(fInput));
}
}
目前这种方式只适用于public字段(看这里)
单个参数测试
如果你只需要一个参数,你不需要用数组来包装它,相反,你可以提供一个可迭代数组或对象数组
@Parameters
public static Iterable<? extends Object> data() {
return Arrays.asList("first test", "second test");
}
或者
@Parameters
public static Object[] data() {
return new Object[] { "first test", "second test" };
}
识别test case个体
为了容易识别各个test case中的测试参数,你可以在@Parameters注解中提供一个名称,此名称允许包含在运行时替换的占位符
- {index}: 当前参数下标
- {0}, {1}, …:第1,2...参数值,注意:单引号'应该转义为双引号''
例子
package com.junit.learning.parameterized;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest3 {
@Parameterized.Parameters(name = "{index}: fib({0})={1}")
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 5 }, { 6, 8 }
});
}
@Parameterized.Parameter // first data value (0) is default
public /* NOT private */ int fInput;
@Parameterized.Parameter(value = 1)
public /* NOT private */ int fExpected;
@Test
public void test() {
assertThat(fExpected).isEqualTo(Fibonacci.compute(fInput));
}
}
加名称之前在idea中运行的效果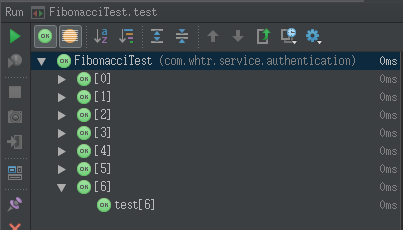
加名称之后在idea中的运行效果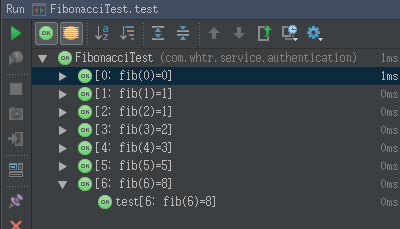
在上面给出的例子中,参数化转轮创建像名称[1:FIB(3)= 2]。如果没有指定名称,当前的参数指标将被默认使用。
参考
参数测试,你还可以看看这里